fzf-native is a c port of fzf. It only covers the algorithm and
implements few functions to support calculating the score.
This means that the fzf syntax is supported:
| Token | Match type | Description |
|---|---|---|
sbtrkt |
fuzzy-match | Items that match sbtrkt |
'wild |
exact-match (quoted) | Items that include wild |
^music |
prefix-exact-match | Items that start with music |
.mp3$ |
suffix-exact-match | Items that end with .mp3 |
!fire |
inverse-exact-match | Items that do not include fire |
!^music |
inverse-prefix-exact-match | Items that do not start with music |
!.mp3$ |
inverse-suffix-exact-match | Items that do not end with .mp3 |
A single bar character term acts as an OR operator. For example, the following
query matches entries that start with core and end with either go, rb,
or py.
^core go$ | rb$ | py$
This is an advantage over the more simpler fzy algorithm, which is also
available for telescope (as native component or as lua component).
To get fzf-native working, you need to build it with either cmake or make. As of now, we do not ship binaries.
Both install methods will be supported going forward.
This requires:
- CMake, and the Microsoft C++ Build Tools on Windows
- CMake, make, and GCC or Clang on Linux and MacOS
Plug 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', { 'do': 'cmake -S. -Bbuild -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release && cmake --build build --config Release' }use { 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', run = 'cmake -S. -Bbuild -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release && cmake --build build --config Release' }{ 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', build = 'cmake -S. -Bbuild -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release && cmake --build build --config Release' }This requires gcc or clang and make
Plug 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', { 'do': 'make' }use { 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', run = 'make' }{ 'nvim-telescope/telescope-fzf-native.nvim', build = 'make' }-- You dont need to set any of these options. These are the default ones. Only
-- the loading is important
require('telescope').setup {
extensions = {
fzf = {
fuzzy = true, -- false will only do exact matching
override_generic_sorter = true, -- override the generic sorter
override_file_sorter = true, -- override the file sorter
case_mode = "smart_case", -- or "ignore_case" or "respect_case"
-- the default case_mode is "smart_case"
}
}
}
-- To get fzf loaded and working with telescope, you need to call
-- load_extension, somewhere after setup function:
require('telescope').load_extension('fzf')This section is only addressed towards developers who plan to use the library (c or lua bindings). This section is not addressed towards users of the telescope extension.
fzf_slab_t *slab = fzf_make_default_slab();
/* fzf_case_mode enum : CaseSmart = 0, CaseIgnore, CaseRespect
* normalize bool : always set to false because its not implemented yet.
* This is reserved for future use
* pattern char* : pattern you want to match. e.g. "src | lua !.c$
* fuzzy bool : enable or disable fuzzy matching
*/
fzf_pattern_t *pattern = fzf_parse_pattern(CaseSmart, false, "src | lua !.c$", true);
/* you can get the score/position for as many items as you want */
int score = fzf_get_score(line, pattern, slab);
fzf_position_t *pos = fzf_get_positions(line, pattern, slab);
fzf_free_positions(pos);
fzf_free_pattern(pattern);
fzf_free_slab(slab);local fzf = require('fzf_lib')
local slab = fzf.allocate_slab()
-- pattern: string
-- case_mode: number with 0 = smart_case, 1 = ignore_case, 2 = respect_case
-- fuzzy: enable or disable fuzzy matching. default true
local pattern_obj = fzf.parse_pattern(pattern, case_mode, fuzzy)
-- you can get the score/position for as many items as you want
-- line: string
-- score: number
local score = fzf.get_score(line, pattern_obj, slab)
-- table (does not have to be freed)
local pos = fzf.get_pos(line, pattern_obj, slab)
fzf.free_pattern(pattern_obj)
fzf.free_slab(slab)This projects implements fzf algorithm in c. So there might be differences in matching. I don't guarantee completeness.
Stuff still missing that is present in fzf.
- normalize
- case for unicode (i don't think this works currently)
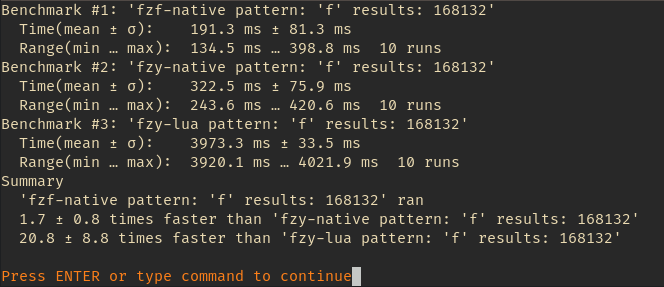
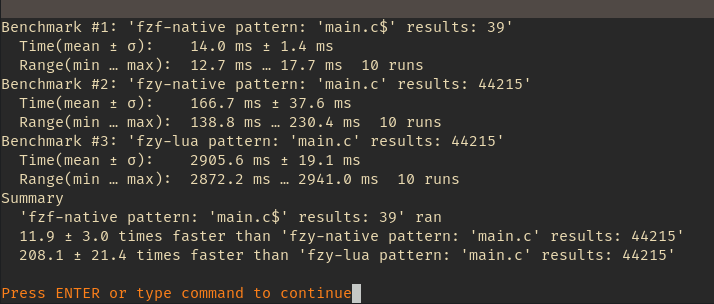
Comparison with fzy-native and fzy-lua with a table containing 240201 file strings. It calculated the score and position (if score > 0) for each of these strings with the pattern that is listed below:
All credit for the algorithm goes to junegunn and his work on fzf. This is merely a c fork distributed under MIT for telescope.