Promise based routing for Express apps. There are 2 parts to this library.
- A promises aware
Routeobject you can extend - A map function to connect routes and resources to
Routeobjects
Most request/response cycles of web apps follow the same pattern
- run some code based on a URL
- potentially reject or redirect based on authorization/authentication
- create, read, update, delete data (aka CRUD)
- present data back to the client
I wanted to abstract the logic of mapping paths to files and have ways to hook into the request/response lifecycle as needed. Instead of having controller objects that manage a group of URLs I found it clearer (and easier to test) to have one object per URL (i.e. UsersShowRoute). If no route object exists it will render the corresponding view. If one does exists it will process the request by stepping through the lifecycle hooks. This lets you add logic to just one part of the request/response process.
npm install --save project-router
app.js
var app = require('express')();
var projectRouter = require('project-router');
// Map paths to route objects
// returns an instance of `express.Router()`
var router = projectRouter.map(function () {
this.get('/', 'pages/index');
});
app.use(router);app/routes/pages/index.js
var Route = require('project-router').Route;
// Extend from the base `Route` object
var PagesIndexRoute = Route.extend({
// Define a model hook (this can return a value directly or a promise)
model: function () { return User.findOne().exec(); }
});
module.exports = PagesIndexRoute;app/views/pages/index.hbs
<p>
The data return (or resolved) from the model hook is now available in the view.
{{username}}
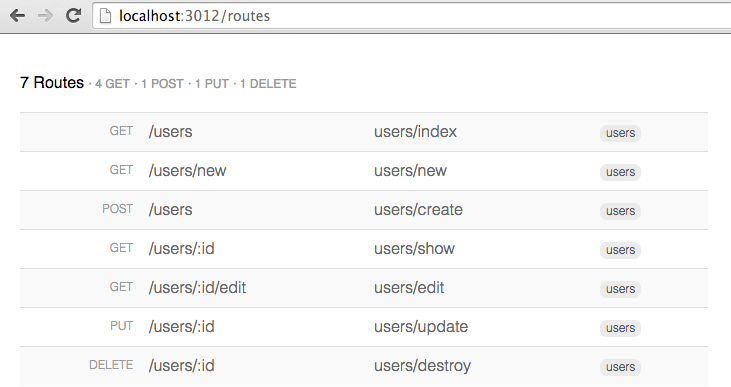
</p>Use Project Router Viewer to see a list of routes.
Route objects are what handle incoming requests. There are a few request/response lifecycle hooks you can define. This pattern was heavily inspired by the Ember Router.
The following are the most useful lifecycle hooks listing in the order they are called. beforeModel, model, and afterModel can optionally return promises. These promises will be resolved before calling the next lifecycle method.
.enter()
The first method that gets called. This is your chance to do somehting synchronous (i.e. reject the request based on data already available).
.beforeModel()
If you return a promise from this method it will be resolved before the model hook gets called. Useful if you have data you need to load asynchronously before getting the model'.
.model()
Should return the data for the route or a promise that resolves to the data.
.afterModel(resolvedModel)
Get passed the result of model. Use this for any logic that depends on having the data (like authorization that can only be determined with the object). This can also return a promise.
.responseData(resolvedModel)
Also gets passed the result of model. This just returns resolvedModel but can be used to transform the repsonse data (serializing, presenting, etc.)
.error(reason)
Catches any promise errors. Calls this.reject(reason) by default.
.reject([code,] error)
Ends request with error. Status code defaults to 400
.redirect()
Delegates to Express response redirect method
.param()
Delegates to Express response param method
.html(data)
Renders this.templatePath with data as context
.json(data)
Sends json response as data
.params()
Returns this.request.params
.body()
Returns this.request.body
.query()
Returns this.request.query
this.request
The Express request object
this.response
The Express response object
this.path
The path defined in router (i.e. '/users/:id')
this.templatePath
The view the route will render. Matches the route filepath by default. this.get('/users, users/index') will render app/views/users/index.hbs. You can define this property to change what template will be rendered (i.e. UsersIndexRoute.prototype.templatePath = 'pages/index;)
this.resource
The resource object (if defined). this.resource('users', {resource: UserModel}) would be UserModel. This can be defined on the router definition in the options hash or on the Route object (i.e. UsersIndexRoute.prototype.resource = UserModel).
this.resourceName
The name of the resource (if defined). this.resource('users') would be users.
var Route = require('project-router').Route;
module.exports = Route.extend({
// Authorize request
enter: function () {
if (!this.request.isAdmin()) this.reject(401, 'Unauthorized');
},
// Some special async admin authorization
beforeModel: function () {
return new RSVP.Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
AdminAuth.canAccess('users', function (canAccess) {
canAccess ? resolve() : reject ();
});
});
},
// Get list of users (assuming this.resource is mongoose model)
model: function () {
return this.resource.findById(this.param('id')).exec();
},
// 404 if model wasn't found
afterModel: function (model) {
if (!model) this.reject(404, 'Not found');
},
// Namespace response
responseData: function (model) {
return { user: model.toJSON() };
}
});Define routes by providing a map function to projectRouter.map(fn).
Maps get, post, put, or delete to a route file.
projectRouter.map(function () {
// Looks for `Route` object at 'app/routes/users/show.js'
// and renders 'app/views/users/show.hbs'
this.get('users/:id', 'users/show');
// If no route is found at 'app/routes/pages/about' it will
// create one and render 'app/views/pages/about.hbs'
// Can be useful when there is no data that needs to be loaded
this.get('pages/about', 'pages/about');
});Creates routes for a resource
projectRouter.map(function () {
// Equivalent to
// this.get('/users', 'users/index');
// this.get('/users/:id', 'users/show');
// this.get('/users/new', 'users/new');
// this.get('/users/:id/edit', 'users/edit');
// this.post('/users', 'users/create');
// this.put('/users/:id', 'users/update');
// this.delete('/users/:id', 'users/destroy');
this.resource('users')
// Control what routes are created with `only` or `except` options
this.resource('users', {only: ['index', 'show']);
this.resource('users', {except: ['desdtroy']);
// Nest a resource by passing a function as the last argument
// Will create paths in this format:
// '/users/:userId/posts/:postId/comments/:id'
// And look for route file or view at
// 'app/routes/users/posts/comments/show.js'
// 'app/views/users/posts/comments/show.hbs'
this.resource('users', function () {
this.resource('posts', function () {
this.resource('comments');
});
});
// Use member and collection to add more actions to a resource
// The following creates:
// '/users/:id/login'
// '/users/active'
this.resource('users', function () {
this.member.post('/login');
this.collection.get('/active');
});
});Creates a namespaced scope for routes
projectRouter.map(function () {
// Equivalent to
// this.get('/api/users', 'api/users/index');
// this.get('/api/posts', 'api/posts/index');
this.namespace('api', function () {
this.get('/users', 'users/index');
this.resource('posts', {only: ['index']});
});
});