implemented sha-256 algorithm using Erlang, That follows client server architecture and actor model in erlang.
Steps to run the program-:
- Download the project1.zip file
- Extract the contents.
- There are two types of files one is to run the program on a local server(dosp1.erl) and the other is to establish a client-server connection to run the workers on different nodes.
- Let’s start with how to run the program on the local server.
- Navigate to cmd and then go to the directory where the file(dosp1) is,
- Type erl,
- It will start the erlang shell
- Type – c(dosp1). (to compile the file)
- Type- ‘dosp1:run(Input).’ (to start the code) ** here input is the number of zeroes u want to test it on so write it like ‘dosp1:run(4).’ If u want to test it to four 0’s.
- ** At most u can mine for 5 zeroes after that the process will take a long time.
- It will look like this-:
- Use ctrl+c to stop the program execution because it will run for an infinite time until the machine resources exhaust completely.
- Now let’s run the code for client-server functionality
- Navigate to cmd and then go to the directory where the file (client.erl and server.erl) is,
- Type erl,
- It will start erlang shell,
- Compile the file,s for that first type- ‘c(client).’ and then type ‘c(server).’
- After compilation is done copy the client file and paste it into another node or machine
- Do the same for the node to compile the client code,
- In the server file on line 10 replace 192.168.0.42 with the IP address of the client and compile it.
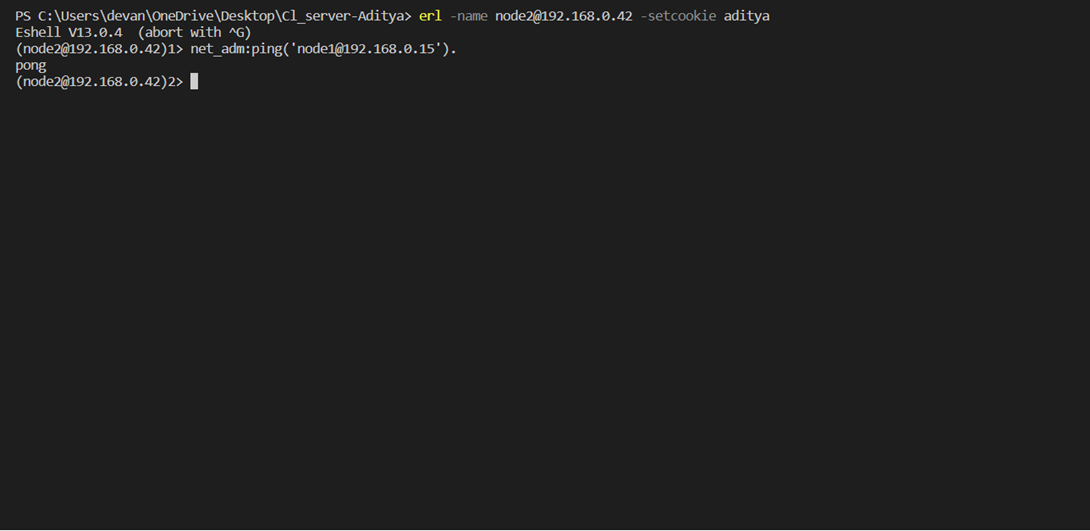
- Now let’s establish the connection On the server side, in the directory type-
- (erl -name node1@’IP_address_of_server_node’ -setcookie ‘name_of_cookie’.)
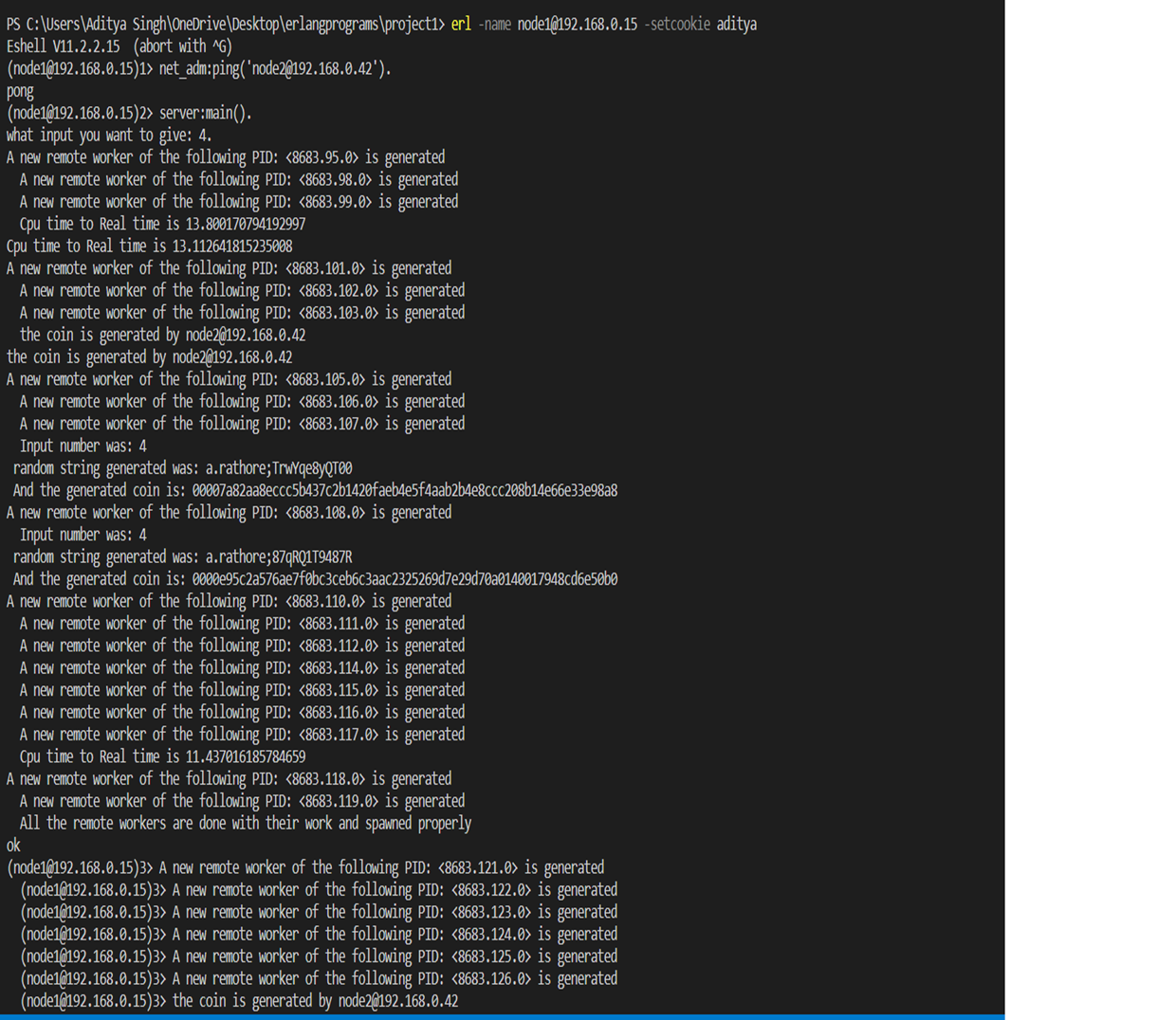
On the client side. In the directory type () 2. (erl -name node2@’IP_address_of_client_node’ -setcookie ‘cookie_name_same_as_server’.) 3. Now to establish the connection, on server type- (net_adm:ping(node2@’IP_address_of_client_node’).) If pong comes as output then the connection is established and now the node will work as a worker and will help in coin hashing.
Refer to the images At the client-
At the server side-
After the connection is done
1.c(server).
2.server:main(). – this will run the main function in the client and will generate workers that will participate in hashing.
As the process is asynchronous, the output will not be in sync as every string take a different amount of time to be mined.
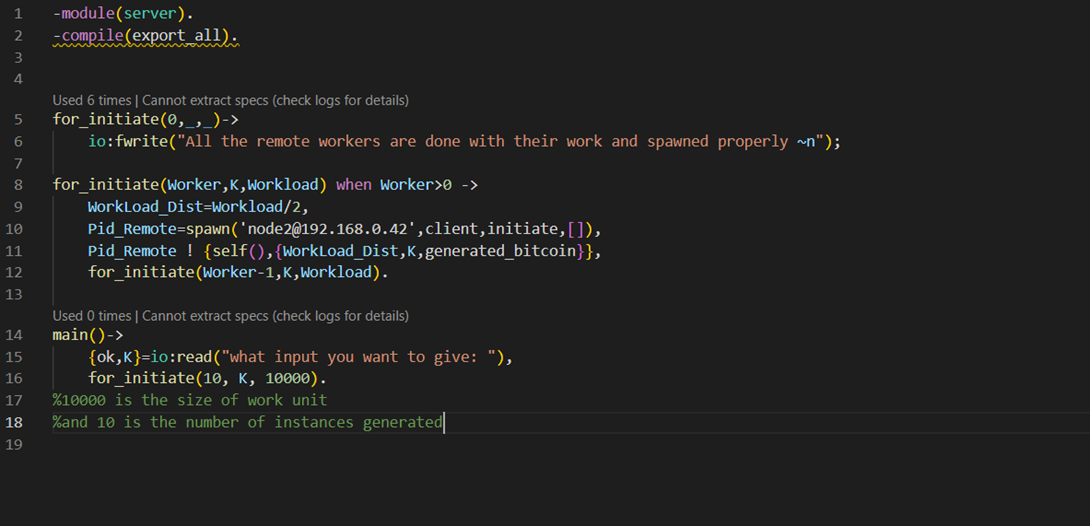
• Question 1- The size of the work unit that you determined results in the best performance for your implementation and an explanation of how you determined it. The size of the work unit refers to the number of sub-problems that a worker gets in a single request from the boss. As we can see in the image, the workload here is 10000 which was divided by every worker and 10 is the number of instances generated, So basically 10000 processes will run on every instance generated. This was for the best performance we can change the number but it may impact performance, and totally vary from machine to machine.
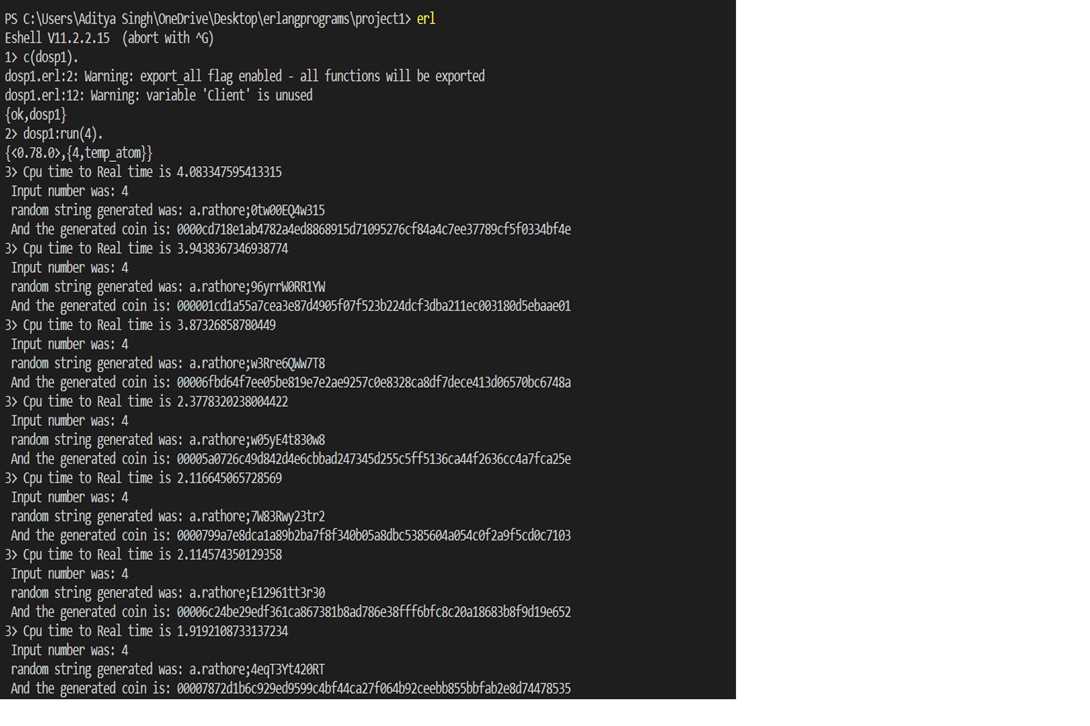
• Question 2- The result of running your program for input 4.
Solution- Here is the result of running with input 4.
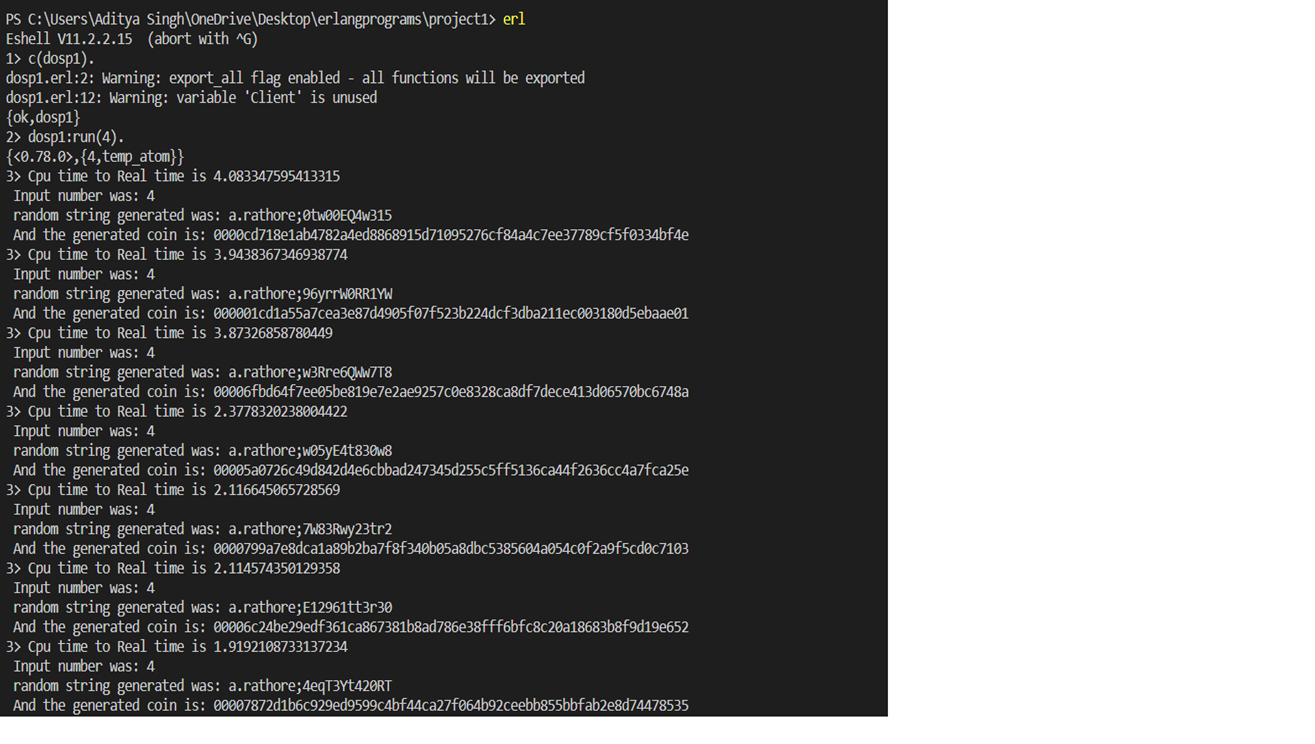
• Question 3-The running time for the above is reported by time for the above and report the time. The ratio of CPU time to REAL TIME tells you how many cores were effectively used in the computation. If you are close to 1 you have almost no parallelism (points will be subtracted). Solution- As we can see in the image above the CPU time to real-time is varying between (2-5).
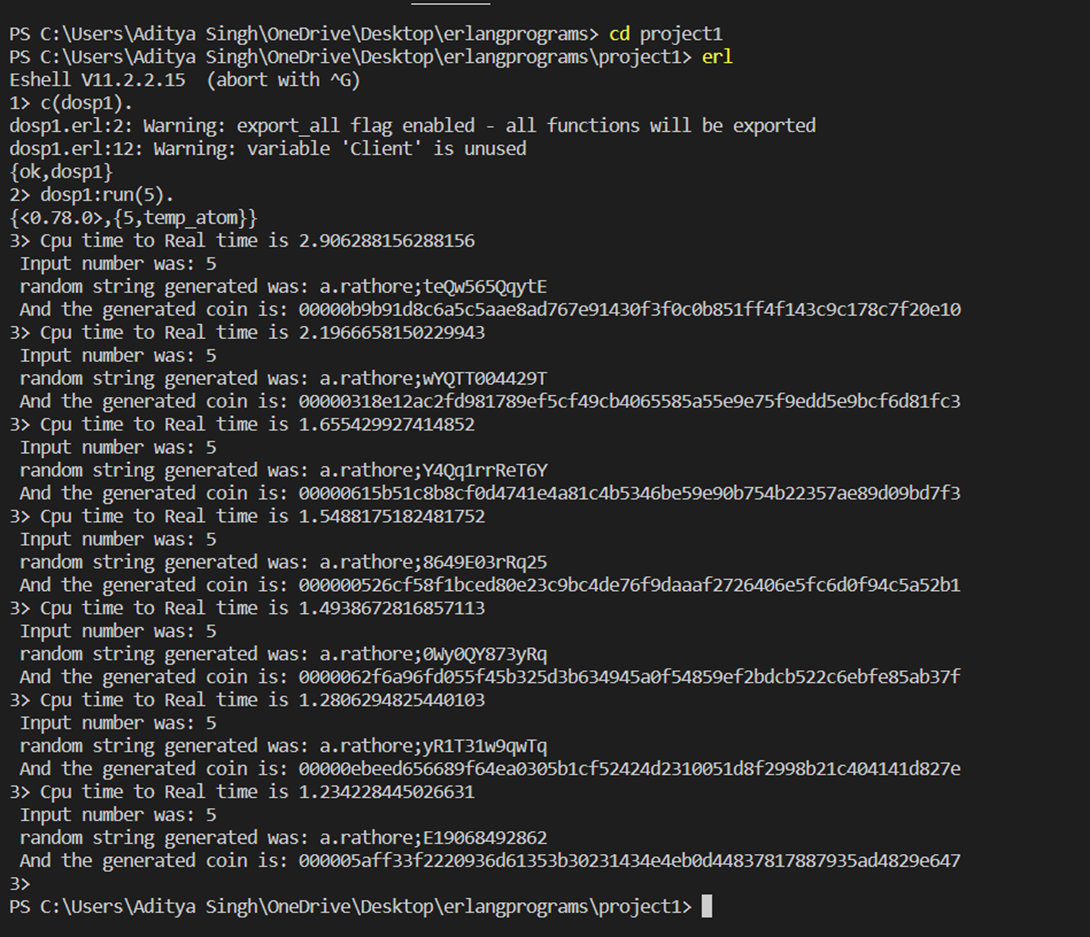
• Question 4- The coin with the most 0s you managed to find. Solution- 5 is the most 0’s we managed to find.
• Question 5- The largest number of working machines you were able to run your code with. Solution- We were able to run our code on 11 machines one was server and other was client.