This is the course header. This will be added on top of every page. Go to DoDAO.io to know more.
Why Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that are pegged to the value of a fiat currency, commodity, or other cryptocurrency. The value of a stablecoin is designed to remain stable, unlike other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin which can experience significant price fluctuations. Examples of stablecoins include Tether, USD Coin, Dai etc. These coins can be used for various applications such as trading, payments and remittances.
One of the most promising benefits of blockchain technology is its ability to provide a global financial system that can settle payments within seconds. A strong and stable global currency is an essential part of a healthy financial system, and over the past few years we've seen many innovative projects come up with ideas for creating tokens that are equivalent to USD or other currencies on the blockchain. Some of these projects have failed, but a few have survived and proven to be very resilient.
There are a few key reasons why stablecoins are seen as a useful tool:
- Improving cross-border transactions: Stablecoins can help facilitate low-cost, fast, and secure cross-border transactions while reducing complexity compared to traditional methods.
- Entry Point: Newcomers to the crypto world often want a stable way to store their money, similar to what they're used to with banks. Stablecoins offer a more predictable and stable path for these people.
- Base Currency : A stablecoins value does not fluctuate as much as other cryptocurrencies, making it a more reliable currency to calculate stocks, transactions, and spends with. This also makes it easier to compare the value of one thing to another.
- Increased adoption : The volatility of other cryptocurrencies can make them difficult to use for everyday transactions or as a means of payment. Stablecoins can make it easier for businesses and individuals to use and accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment, which leads to an increase in adoption.
- Better risk management : Stablecoins can provide an alternative to traditional investments and can be used to hedge against market volatility.
- Decentralized Finance: Stablecoins can be used as collateral, borrowing and lending in decentralized finance platforms which can provide more opportunities for financial inclusion and better returns compared to traditional finance. Type of Stablecoins
In the last few years, many stablecoin projects have been created, each with a different approach to representing the USD on blockchain. Let's first look at the most prominent categories of stablecoins and then understand the advantages and drawbacks of each of these categories.
Fiat-backed stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that is pegged to the US dollar. In this system, each USD-pegged token is backed 1:1 by actual US dollars. This means that fiat-backed stablecoins must be backed by bank accounts that contain USD or other stable currency. As a result, the old financial system's centralized structure and regulated institutions are used by fiat-backed stablecoin issuers.
Since there are no clear regulations governing the production of stablecoins, financial institutions have no specific standards to follow. This lack of transparency can be a major problem for stablecoin issuers, as it leaves them open to exploitative practices.
Stablecoin issuers earn revenue from investing the cash they receive from customers, and use this money to cover their operational expenses. Any money left over after paying for operations is generally profit for the issuer. However, in some cases issuers may choose to invest this money in long-term or risky ventures in order to maximize their profits. This can lead to losses of funds for customers.
It's important for users to understand how stablecoins are backed. What percentage of the backing is in cash, and what percentage is in investments? What types of investments are made by the issuer?
Cryptocurrency-backed stablecoins are a type of digital asset that is backed by other digital assets like BTC, ETH, or other tokens. In order to mint new stablecoins, digital assets are locked up as collateral in smart contracts. DAI from MakerDAO is a well-known example of a stablecoin that is backed by cryptocurrency.
Since crypto prices can be volatile, stablecoins are overcollateralized to ensure that the price stays as stable as possible. This means that a stablecoin with a crypto asset backing of $1 might have an underlying asset worth at least $2. If crypto prices fall, more crypto must be used to back the stablecoin; otherwise, the stablecoins' value would decrease.
There can still be cases where the value of crypto falls and the collateral value becomes lower than the optimal ratio. In these cases, platforms liquidate the position of the borrower (the person who deposits collateral to mint new stablecoins). Different platforms take different approaches to liquidation, some selling the collateral at a fixed discount, and some using American or Dutch options. The amount of collateral to be liquidated also varies from one platform to another.
Commodity-backed stablecoins are similar to fiat-backed stablecoins in that they are backed by physical commodities such as gold, silver, or oil. Even real estate can be used as collateral for commodity-backed stablecoins. The coins may or may not be redeemable for the physical asset. In a sense, commodity-backed stablecoins are a digital representation of a valuable real-world asset.
For those who find it difficult to invest in literal precious commodities, commodity-backed stablecoins can be a useful alternative. These coins are backed by commodities like gold, which gives them the same value as the collateral. They can be liquidated when desired, and because they're not as volatile as fiat or cryptocurrencies, they can be a safer investment.
The "two-coin" system is a typical algorithmic stablecoin structure in which one coin is used to "absorb" market volatility, and the other strives to keep the peg.
Lets assume there are two tokens A_USD, and ALGO. A_USD value remains $1 and ALGO is balancer token which is sold or bought to maintain the peg of A_USD at $1
When the A_USD supply is too small and demand for it is too high, the price of A_USD goes above $1. To bring A_USD back to its peg, the protocol lets users trade 1 A_USD of ALGO for 1 A_USD. This trade burns 1 USD of ALGO and mints 1 A_USD, which users can sell for 1.01 USD and pocket a profit of 1 cent. It doesn’t sound like a lot, but these profits add up when done in large quantities.
When the supply is too large and demand is too low, the opposite happens: The price of A_USD goes below $1. So the protocol lets users do the opposite as above: Users can buy 1 A_USD for 0.99 USD, then trade 1 A_USD for 1 USD of ALGO. The trade burns 1 A_USD and mints 1 USD of ALGO, netting the arbitrage trader a profit of .01 A_USD.
This is how the price of A_USD is maintained at $1 USD
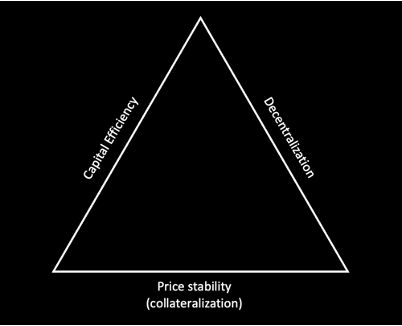
Stablecoin Trilemma
A stablecoin must maintain a delicate balance between three major objectives: price stability, decentralization, and capital efficiency.
Price Stability - Price stability is one of the most important aspects for stablecoins. Fiat-based coins offer the highest price stability, followed by crypto-backed coins and then algorithmic stablecoins. In 2022, we saw the failure of the biggest algorithmic coin, UST.
Importance of Decentralization - Decentralization is important because it allows for more democratic practices around the world. When governments have too much control, they can block users' funds which can cripple a person's ability to speak out or protest against the government. A fully decentralized world would benefit greatly from these democratic practices, and we should strive to not give up on these principles. Even though fiat backed stable coins have excellent price stability, they lack decentralization as they are issued by a centralized issuer.
Capital Efficiency - Capital efficiency defined as how much capital is required to make $1 of a token. In case of algorithmic coins we might not need any real assets, so it has very high capital efficiency. In case of fiat backed stable coins we need 1 USD cash(something similar) to create $1 token. In case of collateralized crypto coins, this value can be as high as 3-4 times i.e. we might need $3-$4 worth of crypto assets as collateral to generate $1 worth of stablecoin token.
Stablecoins Future
At the end of 2022, transactions that only involve the top four largest stablecoins by market capitalization (USDT, USDC, BUSD, and DAI) make up 76% of all trading volume across centralized exchanges, according to CryptoCompare. Fiat-backed stablecoins make up 91.7% of this crypto sector, and Tether (USDT) and USDCoin (USDC) comprise the majority of that, leaving crypto-backed and algorithmic stablecoins to make up the remainder.
Stablecoins have a lot of potential uses that could be really beneficial for mainstream commercial purposes, like merchant payments and cross-border remittances. In fact, we're starting to see more stablecoin payments being sent all over the world via public blockchain networks - which suggests that these assets are not just a store of value for crypto market players, but actually represent an improvement over traditional payment methods. So it's likely that demand for stablecoins will continue to grow in the long term.
That's one of the reasons why we're seeing more DeFi protocols launching their own platform-native stablecoins - as a way to source liquidity and offer integrated services.
For example, the team behind automated market maker Curve has released plans on Github for a new stablecoin design called a Lending-Liquidating AMM Algorithm or LLAMMA. With this design, the collateral type is contingent on price performance. Decentralized lender Aave has also released a technical paper for its upcoming overcollateralized GHO stablecoin. This could help it lower capital efficiency costs.
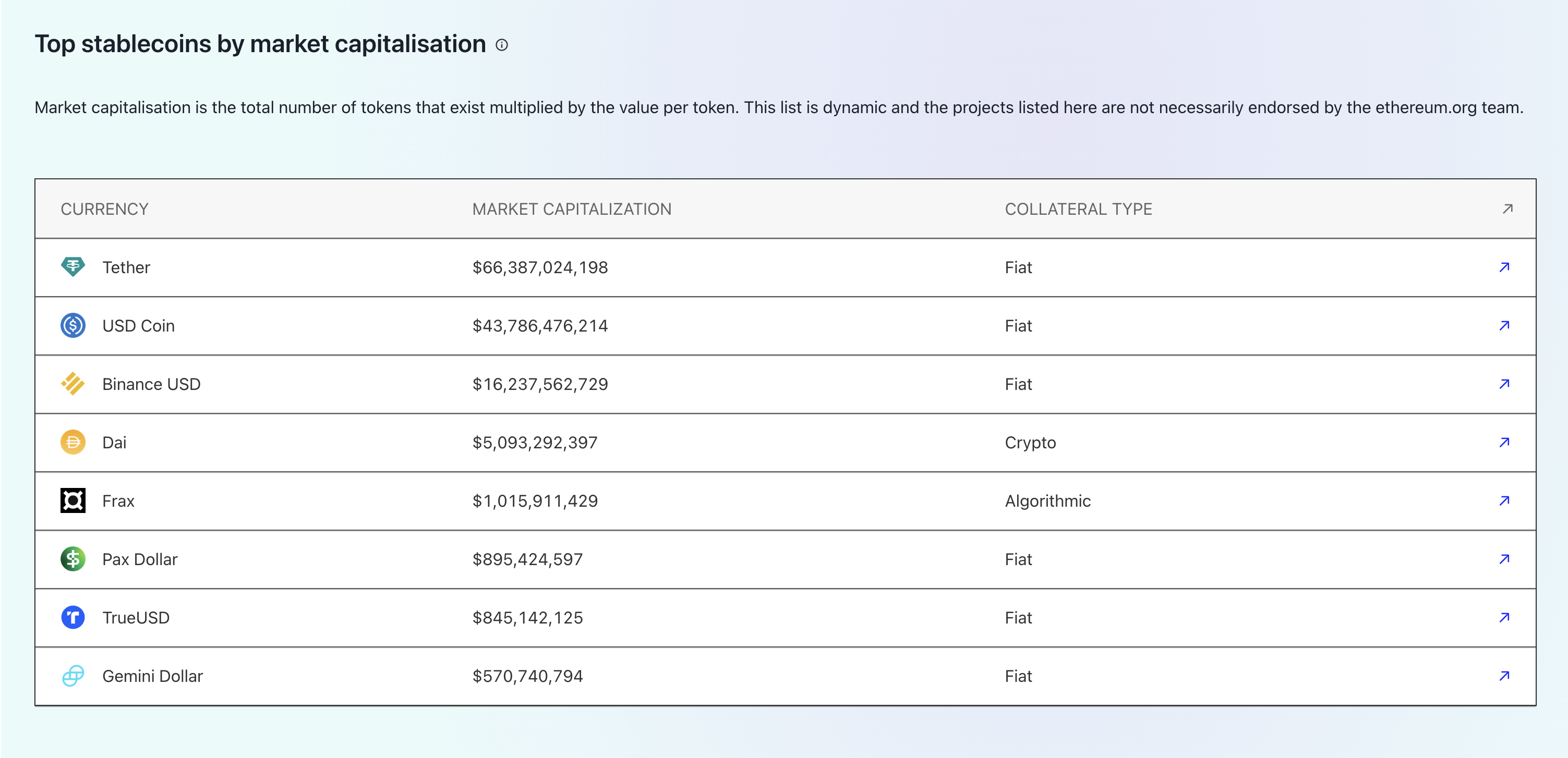
Top Market Cap
The market capitalisation of a project is the total number of tokens that exist multiplied by the value per token. Here are the stable coins that represent the top market capitalisation of stable coins:
Source: https://ethereum.org/en/stablecoins/